Unveiling the nitrogen-rich massive star in the metal-poor galaxy NGC 4068
Abstract
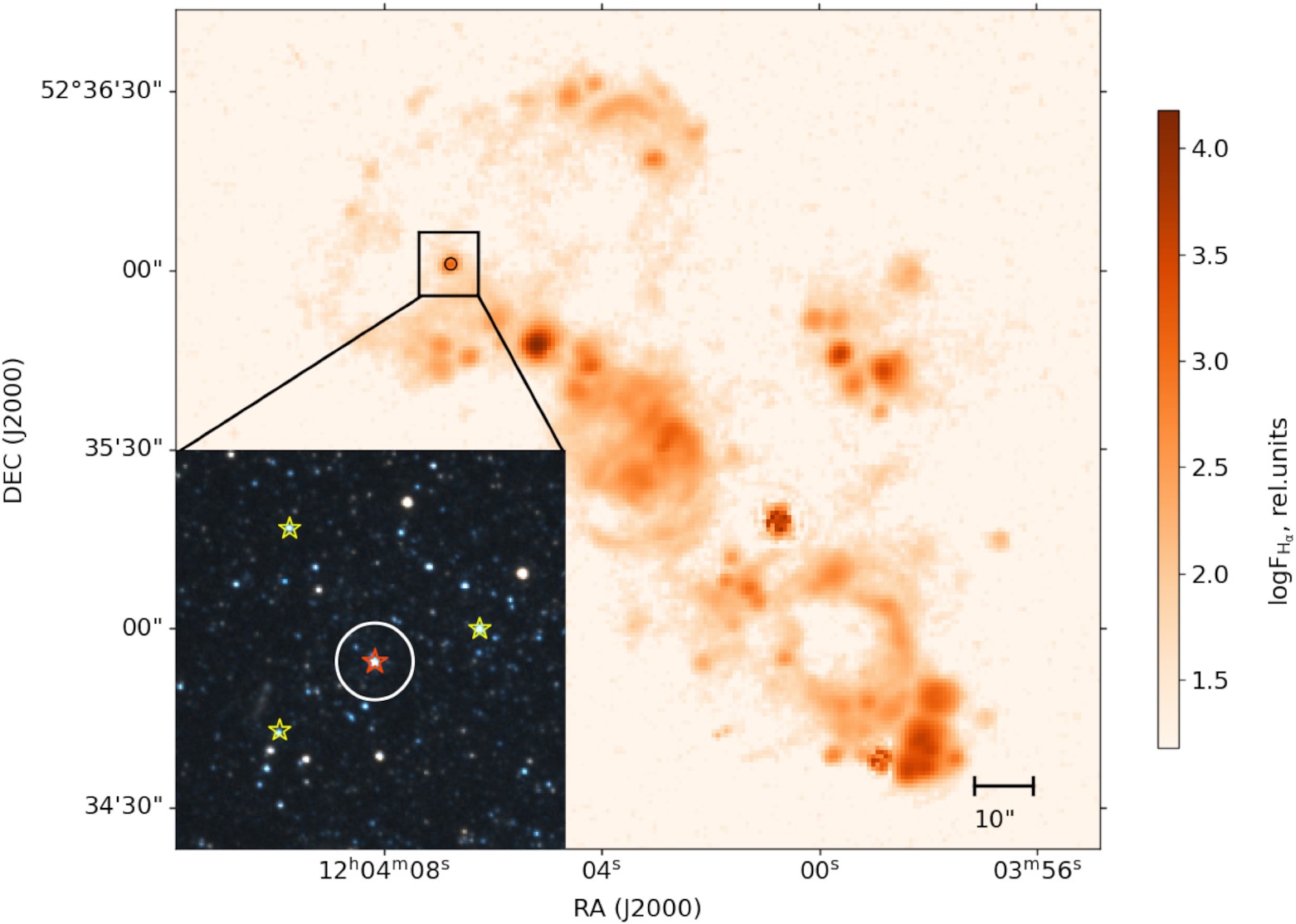
We report the identification of the unusual emission-line stellar-like object in the nearby low-metallicity ($Z \sim 0.1 \, \mathrm{Z_{\odot }}$) dwarf galaxy NGC 4068. Our observations performed with long-slit spectrograph and Fabry-Perot interferometer demonstrate high velocity dispersion in H α line, presence of He II λ4686Å line and peculiarly low [S II]/[N II] fluxes ratio for this object. From observational data, we derived that the object represents a single star of high bolometric luminosity (L* ~ 1.5 × 106 L⊙) surrounded by an expanding nebula with kinematical age of t ~ 0.5 Myr. The nebula exhibits significant nitrogen overabundance [log (N/O) ~ -0.05, that is by ~1.4 dex higher than expected for low-metallicity galaxies]. We suggested that this is a massive blue supergiant (BSG) or Wolf-Rayet (WR) star surrounded by its ejecta interacting with the interstellar medium. We calculated the models of the nebula using CLOUDY photoionization code, applying CMFGEN-modelled BSG and WR stars as ionization sources. We found a best agreement between the modelled and observed spectra for the model assuming ionization by low-metallicity WR star of mass $M_*\approx 80\, \rm M_\odot$, ionizing the nebula through the strong wind and enriching the interstellar medium with nitrogen.
- Publication:
-
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
- Pub Date:
- January 2023
- DOI:
- arXiv:
- arXiv:2209.12522
- Bibcode:
- 2023MNRAS.518.2256Y
- Keywords:
-
- stars: massive;
- stars: Wolf-Rayet;
- ISM: abundances;
- galaxies: individual: NGC 4068;
- Astrophysics - Astrophysics of Galaxies;
- Astrophysics - Solar and Stellar Astrophysics
- E-Print:
- Minor revision